A Mysterious Low-Frequency Sound Has Been Recorded High in the Stratosphere
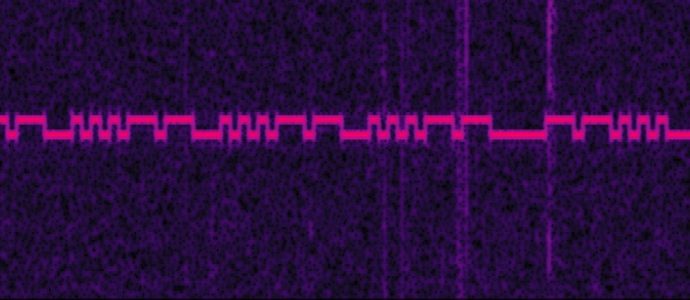
A fleet of DIY solar-powered, high-altitude research balloons have recorded a mysterious low-frequency sound high in the upper atmosphere that repeats a number of times each hour. The sound occurs in the infrasound range, meaning it’s below the threshold of human hearing, only occasionally spiking as high as 25read more